Communication is a process of transferring information from one person (the sender) to another (the receiver).
Channels of Communication
- Formal Channels: used for official matters; disseminate vital info e.g. HR manager's letter to staff.
- Informal Channels: used between people who contact each other regularly e.g, phone call to a colleague to check a customer's address.
- Unofficial Channels: Grapevine is an informal, unofficial and personal communication channel within an organisation. This social network results from rumour or gossip.
Different Channels of Communication: WOVE
WRITTEN: reports, memos, itineraries, bulletins, notices of meetings, ads
ORAL: interviews, meetings, conferences, radio, television, telephone
VISUAL: charts, pictures, body language, multimedia presentations
ELECTRONIC: teleconferencing, videoconferencing, email, telephone and fax
Flow of Communication
Downward, Upward, Vertical, Horizontal
Examples: informing employees of their jobs/responsibilities, instructing employees how to bolster productivity, relaying to employees the results of their job performance.

More examples: transmit information needed for higher-level decision making, give office employees the opportunity to ask questions, make complaints etc.

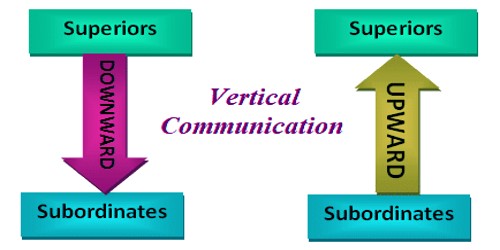
Vertical communication is the flow of information between members of an organisation who are in authority and those who are subordinates. Vertical communication can be used both in a downward and upward direction.
Horizontal communication is also called lateral communication. It involves the flow of of information between individuals and groups on the same level in the organisation.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/what-is-communication-process-1689767_FINAL-069d65e4e1414e5c917379c42a537a66.png)
Communication Cycle
Noise: Barriers to Communication
Literacy skills
Language and semantics
Time constraints/pressure
Personal bias
Cultural bias
What can you do to overcome language/literacy problems, time constraint, personal bias?
Effective Communication
Clear thinking: ability to formulate a well-organised and logical message
Clear speech: speaking clearly and logically
Clear and concise writing: getting the message across
Factors to Consider when Selecting Communication Media
Degree of urgency
Level of confidentiality
Location and distance
Internal/external use
Good or bad news
Why were these Commercials Banned


QUESTIONS
ReplyDelete1. Define a) bias b) culture c) semantics d) barriers e) noise
2. Using a diagram, list 5 steps in the communication cycle.
3. Distinguish between upward and downward communication.
4. Differentiate between vertical and horizontal communication.
5. List 4 channels of communication.
6. Distinguish between formal and informal channels of communication.
7. Identify 4 factors you should consider when selecting communication media.
8. What is communication?